The semiconductor industry is on the cusp of transformative changes, driven by technological innovations, geopolitical tensions, and the ever-evolving demands of the market.
Looking forward to 2024, the semiconductor landscape is set to be shaped by several key trends and developments.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into predictions spanning from regional advancements to cutting-edge technologies and geopolitical shifts.
Read More: 5 Companies Which Revolutionized Semiconductor Industry in 2023
India’s semiconductor industry has long been a nascent player, but 2024 could mark a turning point. With a growing desire for technological independence and heightened US-China tensions, India is set to focus on semiconductor manufacturing. The announcement of increased attention on the region may attract major players such as TSMC or Samsung, fostering partnerships and investments.

India’s foray into semiconductor manufacturing is not limited to a specific domain. While silicon semiconductors remain a crucial focus, the broader spectrum includes power semiconductors and compound semiconductors. This diversified approach aims to cater to a wide array of applications, from consumer electronics to power management and advanced materials.
Despite lacking access to the most advanced EUV (Extreme Ultraviolet) lithography machines from ASML, China’s chipmaker SMIC utilized an older but capable DUV (Deep Ultraviolet) technology. This increased process complexity and reduced efficiency compared to EUV, but still enabled 7nm chip production.
China has been investing heavily in developing its semiconductor industry. This initiative has yielded progress in areas like chip design, materials science, and manufacturing techniques, contributing to the 7nm achievement.
Chips produced using DUV technology in 7nm may not match the performance or efficiency of those made with EUV. This could limit their competitiveness in high-end applications.
While China aims to achieve a 5nm tech node demonstration, challenges lie ahead in mass production. US-China tensions may restrict China’s access to vital equipment and materials, potentially impeding progress. The journey to technological self-sufficiency for China could face headwinds.
Intel’s recent successes in foundry services with 5 nodes in 4 years signal a potential challenge to TSMC’s dominance, especially in high-performance computing. These giants are poised to intensify their rivalry, providing a front-row seat to witness how the dynamics of the semiconductor market unfold.
TSMC leads in advanced process technology, notably with its 3 nm node, while Intel aims to regain competitiveness with its 3 nm process utilizing EUV lithography. TSMC’s dominance extends to manufacturing capacity, boasting a global network of fabs, whereas Intel, traditionally focused on in-house manufacturing, is expanding its foundry business.

TSMC’s diverse customer base, spanning mobile devices, high-performance computing, and automotive sectors, mitigates market-specific risks. In contrast, Intel, historically linked to the PC market, is strategically diversifying into data centers, AI, and IoT to reduce vulnerability to market fluctuations.
Geopolitically, both companies navigate complexities, with TSMC’s global presence providing resilience and Intel’s U.S. base influencing its positioning amidst ongoing U.S.-China trade tensions.
Read more: Intel Foundry, Even if Successful, Will Be Overshadowed by TSMC: Chang
Nvidia is a leader in the AI and data center GPU market, which is expected to continue growing rapidly in the coming years. This growth is being driven by the increasing adoption of AI for tasks such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision, as well as the growing demand for data center capacity for cloud computing, big data analytics, and other applications.
Nvidia is expected to launch a number of new products in 2024. This includes new GPUs for the gaming and data center markets, as well as new AI software and tools. These new products could help Nvidia to further solidify its market position and drive revenue growth.
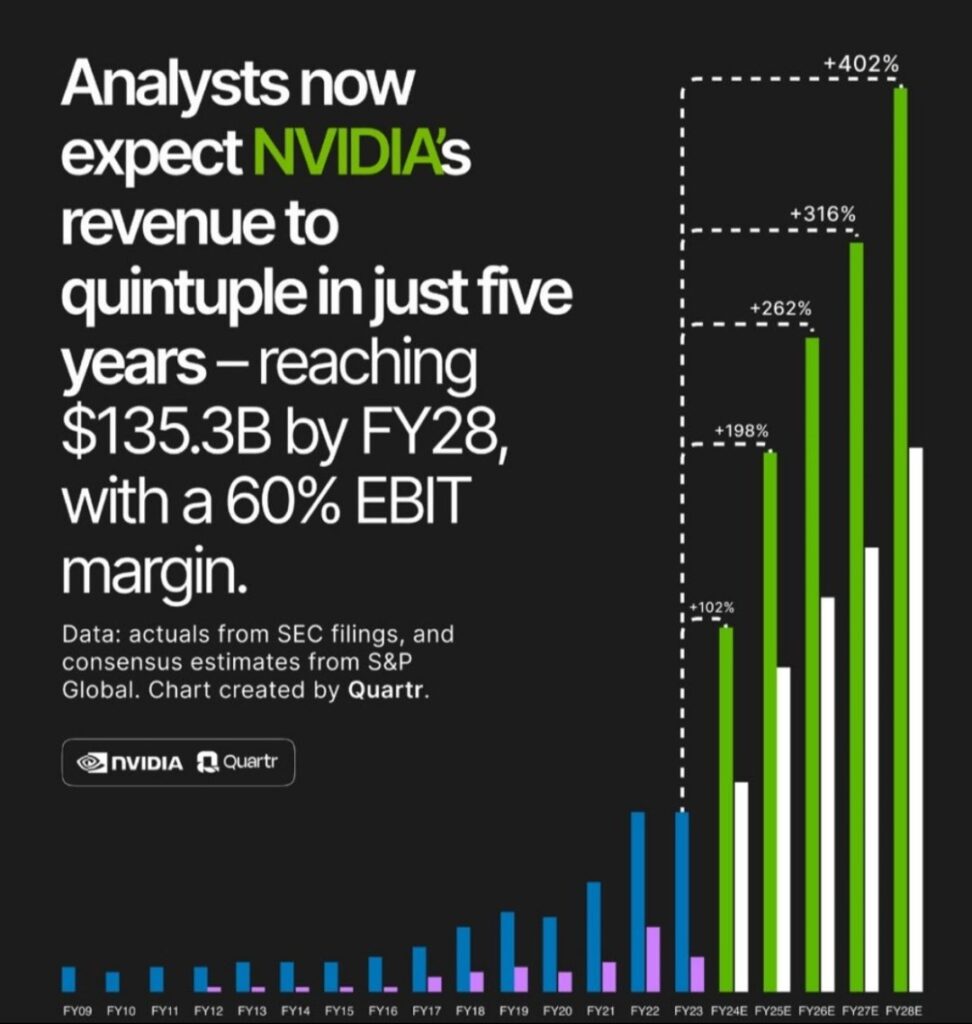
Nvidia faces increasing competition from other chipmakers, such as Intel and AMD.
Read More: What is the Secret Weapon of AMD to Challenge NVIDIA in AI Market
There are several factors driving a renaissance in Japan’s semiconductor industry: TSMCis building a $7 billion fab in Kumamoto, Japan. Expected to commence production in 2024, this plant will manufacture advanced 3nm and 5nm chips crucial for smartphones, high-performance computing, and artificial intelligence.

The Japanese government has committed to investing heavily in the semiconductor industry, with a goal of doubling its chip production capacity by 2030. This includes funding for research and development, as well as subsidies for chipmakers.
Canon, a Japanese company known for its cameras and printers, is making a comeback in the lithography market. Lithography is the process of etching circuits onto silicon wafers, and Canon is developing Nano Imprint lithography machines, which are essential for producing the most advanced chips as a rival to ASML.
In 2024, the semiconductor industry stands at a crucial juncture, influenced by technology, geopolitics, and market dynamics. Predictions for this pivotal year offer insights into the industry’s future. Stay vigilant as these developments unfold, molding the trajectory of a vital modern-era industry.
